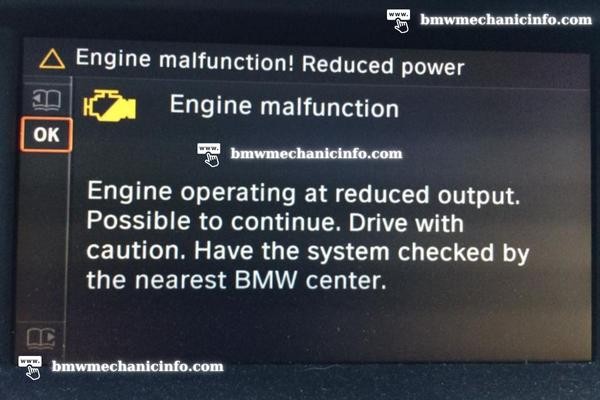
If you notice a BMW engine malfunction reduced power message on your dashboard, there’s likely an underlying problem with your car’s engine. It could be a severe issue, so it’s best to get it diagnosed and fixed promptly.
Several components, including Valvetronic, Vanos, and oxygen sensors, can cause this warning lightly. To identify which system is causing your BMW engine malfunction reduced power output, it’s best to connect an OBD-II scanner and read any error codes generated by that system.
BMW engine malfunction reduced power warning may be caused by the oxygen sensor
The oxygen sensor is one of the most essential parts of your car’s emissions system. It continuously measures oxygen levels in exhaust gases to help the engine computer adjust the air-to-fuel ratio. If something goes awry, it may trigger the check engine light.
A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to various issues, such as rough idling, poor acceleration, and an illuminated check BMW engine malfunction reduced power warning light. If your check engine light has come on, contact an experienced technician immediately for further evaluation. Oxygen sensors are located near your engine’s exhaust pipe and before the catalytic converter to regulate fuel and oxygen mixtures. They generate a voltage your engine computer uses to detect rich or lean mixtures.

When your vehicle’s system works optimally, your car should have a 14.7:1 oxygen-to-fuel ratio. This setting ensures a clean and efficient engine that runs at peak performance. When your vehicle’s ratio of air and fuel fails, it could produce either too much or too little gas, depending on the mixture. This could result in decreased fuel economy and higher emissions.
Newer cars and trucks typically feature multiple oxygen sensors. These may include an upstream and downstream sensor in the exhaust pipe closer to the engine and before the catalytic converter.
Use an OBD2 scan tool like the FIXD Sensor to view readings to verify your oxygen sensor functions correctly. The FIXD Sensor will show the voltage your O sensors produce and their response time. Once you’ve tested your O2 sensor, knowing when to replace it is essential. In newer cars and trucks, most O2 sensors last 60,000-90,000 miles. However, your sensor might only last 90,000 or fewer miles on older vehicles.
If you suspect your oxygen sensor may malfunction, contact Firestone Complete Auto Care immediately to arrange for a full engine inspection and detailed report that pinpoints the source of your car’s BMW engine malfunction reduced power problem. Addressing this problem early will protect both your car’s engine and emissions systems, as well as protect both you and your wallet from further harm.
BMW engine malfunction reduced power warning may be caused by the ignition coil
The ignition coil is an essential element of a vehicle’s system, converting low-voltage output from the battery into higher voltage, igniting pressurized fuel/air mixture in the combustion chamber. This coil features a laminated iron core with an inner secondary winding wrapped in copper wire for insulation. As such, it boasts a meager ohmic resistance (between 0.2 to 3.0 O on the primary side and 5-20 kO on the secondary).
A small amount of current is passed through this circuit, creating a magnetic field around the core and then inducing a higher voltage in the secondary winding that travels to the spark plug. This voltage jumps between electrodes on the spark plug, sparking the fuel/air mixture.

Ignition coils are susceptible to deterioration and failure for several reasons. Vibration can break their internal insulation and cause shorts in their windings, and overheating, which reduces their ability to conduct electricity, are just two examples.
Another common cause of ignition coil failure is misfiring. This may be caused by a damaged spark plug or a worn gap between two electrodes on the pin. In such cases, more voltage must be generated to bridge this gap, creating a short and defective spark. An ignition coil malfunction can also be due to overheating in the engine, leading to a secondary winding breakup. In such cases, it is imperative to replace all coils at once.
An issue can also cause a malfunctioning coil with the timing chain, which controls how many valves open and close to allow air into and out of the engine. A timing chain that has jumped a tooth or more may cause rattling sounds, BMW engine malfunction reduced power warning signs, and check engine lights to illuminate. In such cases, it’s recommended that you get your car diagnosed and repaired by a mechanic as soon as possible.
BMW engine malfunction reduced power warning may be caused by the timing chain
The timing chain is an essential element of the BMW engine, linking the crankshaft to camshaft rotation. It also controls valve timing on cylinder heads and piston timing in combustion chambers. This chain consists of links that move over toothed sprockets that can wear or stretch over time; any signs of wear should be addressed immediately.
Chains can deteriorate to the point that they emit a loud rattling when cold starts when oil pressure and flow are at their lowest points. However, as the oil warms up, this noise may disappear or diminish in volume. Noises in the timing chain are usually due to excessive slack. A hydraulic timing chain tensioner can help reduce this slack. Still, a BMW engine malfunction reduced power check engine light may illuminate if its links have become so loose that the tensioner cannot adjust correctly.
If this occurs, a timing belt or chain assembly may need to be replaced immediately. A broken or snapped chain could cause significant internal damage, likely requiring engine replacement. Another possible issue is that a boost solenoid, an electronic device controlling boost pressure, failed. If this occurs, low boost levels cause acceleration to become sluggish or difficult to start.
An issue with the high-pressure fuel pump or injectors can also cause this error code, making the engine difficult to start or resulting in a rough idle and turning on the yellow check engine light. You should take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair. A complete system scan with an OBD-II scanner will likely be necessary to identify the source of the issue.
Signs that should be observed include poor fuel economy, difficulty starting the engine, and a shaking sensation while accelerating. Furthermore, the engine may misfire or make unusual noises; you might also detect a pungent smell from the exhaust pipe.
BMW engine malfunction reduced Power warning may be caused by the Valvetronic
Many BMW owners will encounter a “BMW engine malfunction reduced power” warning on the instrument panel. This error message usually appears along with the check engine light and can be caused by several issues. To determine the cause of this issue, attach an OBD-II scanner to your car and read its fault codes. This will indicate a problem with Valvetronic or something else entirely.
Valvetronic is an electronic system installed in BMW engines to control intake valve lifts and improve fuel economy and throttle response. According to BMW, it uses an electronically driven eccentric shaft and intermediate lever to regulate valve lifts, eliminating the need for a throttle plate while increasing fuel economy by up to 10% under real-world driving conditions.
This system was introduced in 2002 and has undergone several improvements to improve efficiency. The significant modification involved adding a roller at the interface between the eccentric shaft and intermediate lever; this design was intended to reduce wear issues with previous generations of Valvetronic.
At the time of design, this mechanism allowed for a minimum opening of only 0.4mm – too small to provide adequate airflow when idle. As such, engines that drew too much air could experience performance issues.
However, this is no longer the case. Modern systems feature a lower minimum opening requirement which helps avoid this issue from arising in the first place. Even with proper alignment, an eccentric shaft can still over-travel and cause problems in certain circumstances. If the system fails to keep the eccentric shaft in its intended position, a 2A61 or 2A63 error code will appear on your dash display.
If this code is displayed, the next step is to perform a relearn on the eccentric shaft sensor. Doing so will reset any limit stops to guarantee that the eccentric shaft stays secure.





